Batch Module¶
Contents
Introduction¶
The Batch Module is an implementation of the Spring Batch, which is a framework for dealing with batch processing - reading and processing large amounts of data. Batch Module essential functions are scheduling, triggering and processing the jobs. It allows to schedule and automate basic batch operations so they can be executed without any user interaction.
Setup¶
Batch Module is ready for use right after installation. You can make sure that service is up by sending HTTP GET call to:
http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/ping
In response you should receive HTTP success (2xx) code with response body being string informing about number of jobs.
Defining job¶
To define a job you will have to create job xml config file and a class implementing Batchlet interface to handle that
job. Your job xml file must be placed in META-INF/batch-jobs folder on classpath of module which will define Batchlet.
The name of the config file has to match the name of your job. For example, to define simple logAnalysis job, create logAnalisys.xml
file in META-INF/batch-jobs of your module. Content of logAnalisys.xml could look like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<job id="logAnalysis" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" version="1.0">
<step id="report">
<batchlet ref="org.motechproject.batch.service.impl.LoggingBatchlet"/>
</step>
</job>
job id is just a name of your job, which must be the same as xml filename. step id is a name of the step - each
job contains one ore more steps which are executed within the job. In each step, the corresponding batchlet will execute its
process method. batchlet ref points to batchlet which should be used in this step. Batchlet class should look like in
the example below:
public class LoggingBatchlet implements Batchlet {
@Override
public String process() {
System.out.println("Processing Batchlet");
return "Step executed";
}
@Override
public void stop() {
}
}
Batchlet interface defines two methods to override - process() and stop(). The process() is called everytime
the job step is executed. The stop() is invoked by the Batch runtime as part of JobOperator.stop() method processing.
This simple example will print “Processing Batchlet” string on standard output each time the logAnalysis runs.
Jobs API¶
After a job is defined, you can interact with it in two ways - by HTTP REST calls or with OSGi services, exposed by the Batch module. The exposed services are:
JobService:
public interface JobService {
BatchJobListDTO getListOfJobs() throws BatchException;
void scheduleJob(CronJobScheduleParam params) throws BatchException;
void scheduleOneTimeJob(OneTimeJobScheduleParams params) throws BatchException;
void updateJobProperty(String jobName, Map<String, String> paramsMap) throws BatchException;
long countJobs();
void rescheduleJob(String jobName, String cronExpression);
void unscheduleJob(String jobName) throws BatchException;
}
JobTriggerService:
public interface JobTriggerService {
long triggerJob(String jobName) throws BatchException;
JobExecutionHistoryListDTO getJobExecutionHistory(String jobName) throws BatchException;
long restart(String jobName, Integer executionId) throws BatchException;
}
You can find the description of REST endpoints and services API below.
Getting jobs list¶
Retrieving list of scheduled jobs can be done:
- by HTTP REST call:
GET http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/jobs
or
- using
jobService.getListOfJobs().
In case of REST call, JSON-formatted text, containing list of scheduled jobs will be returned. JobService returns BatchJobListDTO,
which contains field batchJobDtoList being a list of BatchJobDTO. Both JSON representation and BatchJobDTO
contain fields described below:
| Parameter | Type in BatchJobDTO | Description |
|---|---|---|
| jobId | long | Id of the job. |
| jobName | String | Name of the job. |
| cronExpression | String | Cron expression used for scheduling this job. |
| status | String | Status of the job. The job can have ACTIVE or INACTIVE status. |
| parameters | Map<String, String> | Map of parameters with which job is executed (if any). |
| createTime | DateTime | Time of the job creation. |
| lastUpdated | DateTime | Time of the last job update. |
| createdBy | String | Author of the job. |
| lastUpdatedBy | String | Author of the last job update. |
Note
Only scheduled jobs will be returned. If job was defined but not scheduled, it won’t be on the list.
Getting job history¶
Retrieving history of the job, which includes information about each execution of selected job, can be done:
- By HTTP REST call:
GET http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/jobHistory?jobName={jobName}
or
- using
jobTriggerService.getJobExecutionHistory(String jobName)
where jobName is the name of the job for which history should be retrieved.
In case of REST call, JSON-formatted text, containing list of job executions will be returned. JobTriggerService returns
JobExecutionHistoryListDTO, which contains field jobExecutionHistoryList being a list of JobExecution. Both
JSON representation and JobExecution contain fields described below:
| Parameter | Type in JobExecution | Description |
|---|---|---|
| startTime | Date | Time at which job execution started. |
| endTime | Date | Time at which job execution ended. |
| createTime | Date | Time at which job execution was created. |
| exitStatus | String | Status with which execution has ended. |
| jobParameters | Properties | Parameters of the job for this execution. |
| jobName | String | Name of the job. |
| batchStatus | BatchStatus | Batch status of this execution. It’s one of the possible statuses: ABANDONED, COMPLETED, FAILED, STARTED, STARTING, STOPPED, STOPPING. |
| executionId | long | Id of this execution. |
| lastUpdatedTime | Date | Time at which job execution was last updated. |
Triggering job¶
It is possible to trigger a job to execute immediately. This can be done:
- By HTTP REST call:
POST http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/trigger?jobName={jobName}
or
- using
jobTriggerService.triggerJob(String jobName)
where jobName is the name of the job which should be executed. If job requires parameters to run, parameters
from the database will be used.
Scheduling job¶
Job can be scheduled using cron expression. This can by done:
- By HTTP REST call:
POST http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/schedulecronjob
with content type set to application/json and request body JSON structured as shown below:
{
"jobName": "yourJobName",
"cronExpression": "0 15 10 ? * *",
"paramsMap": {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}
}
or
- using
jobService.scheduleJob(CronJobScheduleParam params)
CronJobScheduleParam contains fields with names corresponding to the JSON fields. Find description of them in the table below:
| Parameter | Type in CronJobScheduleParam | Description |
|---|---|---|
| jobName | String | The name of the job to schedule. |
| cronExpression | String | Cron expression which will be used to schedule the job. |
| paramsMap | Map<String, String> | Map of parameters needed by the job to execute. |
Rescheduling job¶
Already scheduled job can be rescheduled with a new cron expression. This can be done:
- By HTTP REST call:
POST http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/reschedulecronjob?jobName={jobName}&cronExpression={cronExpression}
or
- using
jobService.rescheduleJob(String jobName, String cronExpression)
where jobName is the name of the job which should be rescheduled and cronExpression is a new cron expression for
this job.
Unscheduling job¶
Already scheduled job can be unscheduled. This can be done:
- By HTTP REST call:
POST http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/unschedulecronjob?jobName={jobName}
or
- using
jobService.unscheduleJob(String jobName)
where jobName is the name of the job which should be unscheduled.
Scheduling one time job¶
It is possible to schedule a job to run only once at a particular time. This can be done:
- By HTTP REST call:
POST http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/scheduleonetimejob
with content type set to application/json and request body JSON structured as shown below:
{
"jobName": "yourJobName",
"date": "10/10/2016 10:10:10",
"paramsMap": {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}
}
or
- using
jobService.scheduleOneTimeJob(OneTimeJobScheduleParams params)
OneTimeJobScheduleParams contains fields with names corresponding to the JSON fields. Find description of them in the table below:
| Parameter | Type in OneTimeJobScheduleParams | Description |
|---|---|---|
| jobName | String | The name of the job to schedule. |
| date | String | Particular date to run the job. Passed in dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss format. |
| paramsMap | Map<String, String> | Map of parameters needed by the job to execute. |
Updating job parameters¶
Job parameters can be updated:
- By HTTP REST call:
POST http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/updatejobproperty
with content type set to application/json and request body JSON structured as shown below:
{
"jobName": "yourJobName",
"paramsMap": {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}
}
or
- using
jobService.updateJobProperty(String jobName, Map<String, String> paramsMap)
where jobName is the name of the job which should be updated and paramsMap is a map of new parameters for this job.
The parameters map sent in request is compared with existing parameters for the job. If for any parameter the key exist
then its value is updated, else new parameter is added for that job.
Restarting job execution¶
Execution of a batch job can be restarted. This can be done:
- By HTTP REST call:
POST http://{motech-server}/{motech-war-file}/module/batch/restart?jobName={jobName}&executionId={executionId}
or
- using
jobTriggerService.restart(String jobName, Integer executionId)
where jobName is the name of the job and executionId is the ID of the execution to restart.
Database structure¶
The Batch Module creates tables in Motech Data Services database. The structure of those tables is shown on schema below:
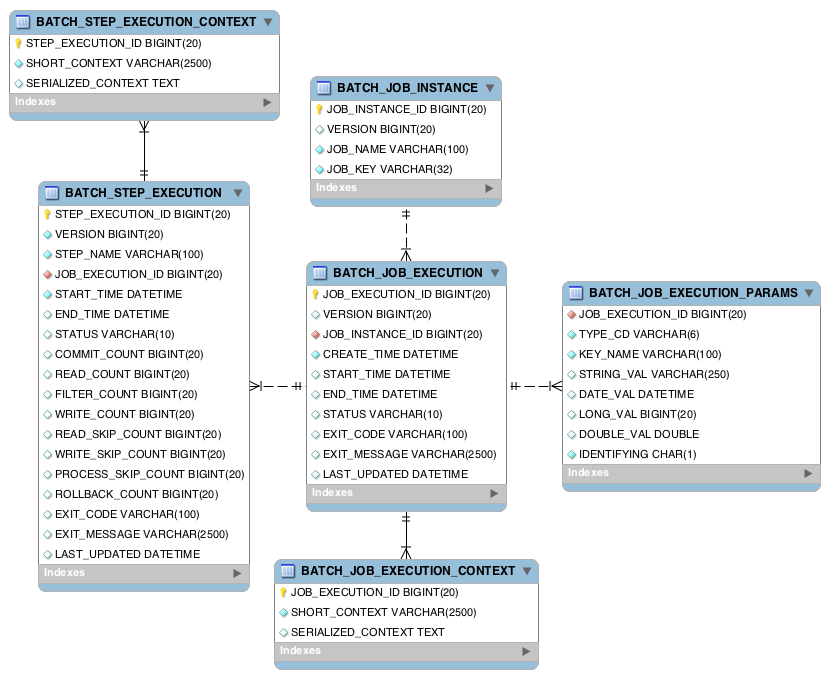
Error handling¶
Errors that occur when using Batch module are wrapped in a custom BatchException exception class. This class contains
reason field that contains description of what caused failure and batchErrors field, which contains BatchErrors
object.
BatchErrors object contains more detailed information about error, which are message, code and httpStatus.
Please refer to table shown below for detailed description of these fields.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| message | String | Short message describing an error. |
| code | int | Custom error code for this error. For possible error codes and meaning of them please refer to the next table. |
| httpStatus | HttpStatus | Http status associated with an error. |
Batch module defines custom error codes, you can find description of them in the table below.
| Code | HttpStatus associated with the error | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1001 | 400 Bad Request | One or more input parameter(s) may be wrong. |
| 1002 | 400 Bad Request | Job not found. |
| 1003 | 400 Bad Request | Duplicate Job. |
| 3001 | 500 Internal server error | Error in starting job. |
| 3002 | 500 Internal server error | Error while reading from or writing to the file. |
| 3003 | 500 Internal server error | Error in querying database. |
| 3004 | 500 Internal server error | Error in unscheduling job. |